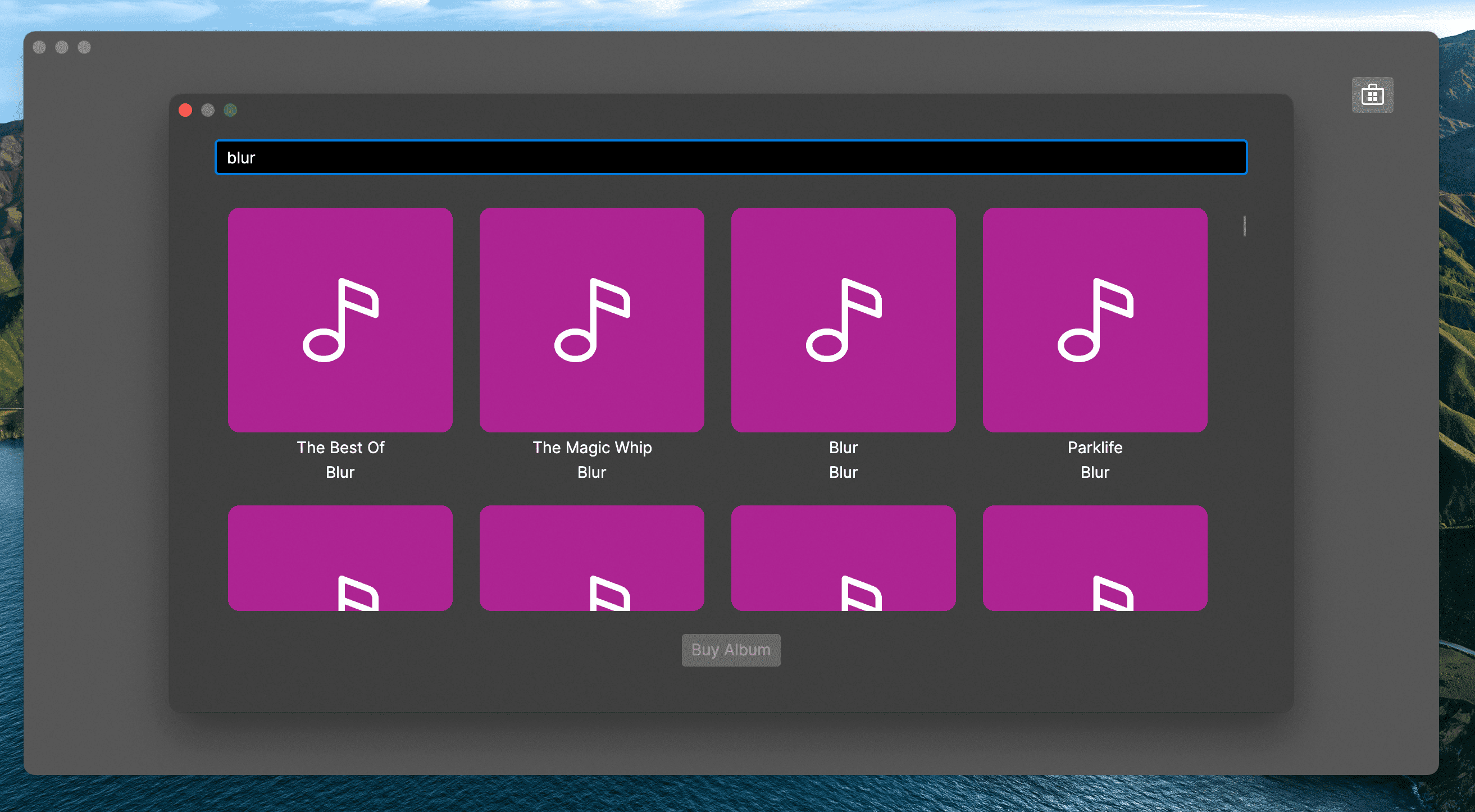
Searching for Albums
Searching For Albums
In order for our application to work we are going to need some business logic. This code is not relevant to the tutorial, except for the fact that it will provide the following services:
- Searching Apple Itunes web api for Albums
- Downloading Album art from the Itunes API.
- Saving / Loading the Albums the user has bought to / from disk.
To add this business logic we need 2 steps.
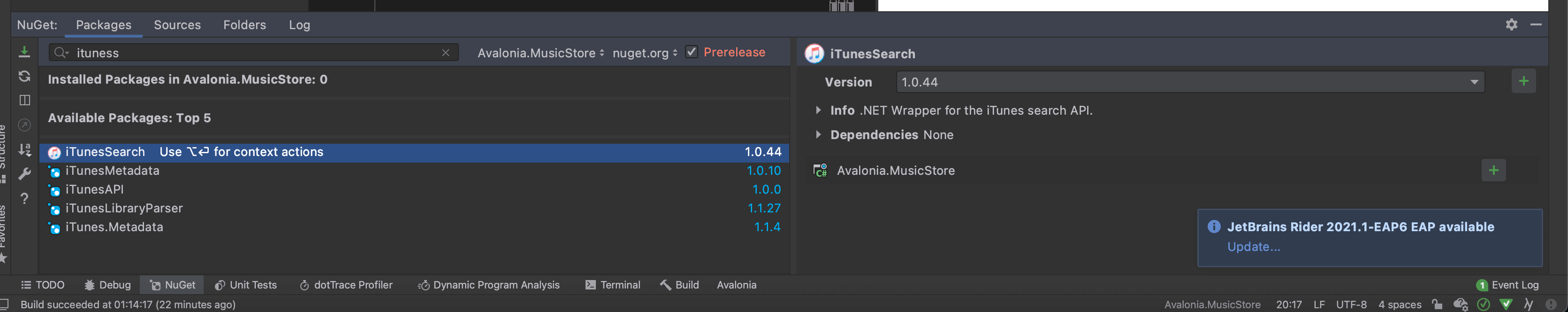
- Add the ItunesSearch nuget package to the project. In Rider right click on our project and select
Manage Nuget Packages
This will open the Packages tool at the bottom of the IDE, like so.
Search for ItunesSearch and press the green + button on the right hand side to install it.
- In the
Modelsfolder add a new class calledAlbumand paste in the following code.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using iTunesSearch.Library;
namespace Avalonia.MusicStore.Models
{
public class Album
{
private static HttpClient s_httpClient = new();
private static iTunesSearchManager s_SearchManager = new();
public Album(string artist, string title, string coverUrl)
{
Artist = artist;
Title = title;
CoverUrl = coverUrl;
}
public string Artist { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string CoverUrl { get; set; }
private string CachePath => $"./Cache/{Artist} - {Title}";
public async Task<Stream> LoadCoverBitmapAsync()
{
if (File.Exists(CachePath + ".bmp"))
{
return File.OpenRead(CachePath + ".bmp");
}
else
{
var data = await s_httpClient.GetByteArrayAsync(CoverUrl);
return new MemoryStream(data);
}
}
public async Task SaveAsync()
{
if (!Directory.Exists("./Cache"))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory("./Cache");
}
using (var fs = File.OpenWrite(CachePath))
{
await SaveToStreamAsync(this, fs);
}
}
public Stream SaveCoverBitmapStream()
{
return File.OpenWrite(CachePath + ".bmp");
}
private static async Task SaveToStreamAsync(Album data, Stream stream)
{
await JsonSerializer.SerializeAsync(stream, data).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
public static async Task<Album> LoadFromStream(Stream stream)
{
return (await JsonSerializer.DeserializeAsync<Album>(stream).ConfigureAwait(false))!;
}
public static async Task<IEnumerable<Album>> LoadCachedAsync()
{
if (!Directory.Exists("./Cache"))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory("./Cache");
}
var results = new List<Album>();
foreach (var file in Directory.EnumerateFiles("./Cache"))
{
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(new DirectoryInfo(file).Extension)) continue;
await using var fs = File.OpenRead(file);
results.Add(await Album.LoadFromStream(fs).ConfigureAwait(false));
}
return results;
}
public static async Task<IEnumerable<Album>> SearchAsync(string searchTerm)
{
var query = await s_SearchManager.GetAlbumsAsync(searchTerm).ConfigureAwait(false);
return query.Albums.Select(x =>
new Album(x.ArtistName, x.CollectionName, x.ArtworkUrl100.Replace("100x100bb", "600x600bb")));
}
}
}
Now that we have the backend code, we can query for Albums as the user types.
Open MusicStoreViewModel.cs and add the following code to the constructor.
this.WhenAnyValue(x => x.SearchText)
.Throttle(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(400))
.ObserveOn(RxApp.MainThreadScheduler)
.Subscribe(DoSearch!);
The WhenAnyValue method is provided thanks to Reactive UI and it takes a lambda expression of the property we want to Observe. By selecting the SearchText property we will fire an event when ever the user types.
Since users can type quite quickly it is not a good idea to try and run a search on every keypress. This is where the Throttle call comes in. Throttle is built into .NET and it takes a TimeSpan in this case 400 milliseconds.
This means we will only see a value if the user has stopped typing for 400 milliseconds or longer.
The final call ObserveOn is required to ensure that our DoSearch method is called on the UIThread. The UI must only be updated on the UI thread. The Throttle call can cause the result to be emitted on some random thread, ObserveOn dispatches it back to the UIThread.
Our AlbumViewModel will need some properties to hold the artist name and album title. Note that because these properties will not change in the UI during runtime, we do not need to use the RaiseAndSetIfChanged method. We can simply expose them as plain get only properties.
Change the AlbumViewModel code so that it matches the following.
private readonly Album _album;
public AlbumViewModel(Album album)
{
_album = album;
}
public string Artist => _album.Artist;
public string Title => _album.Title;
Now our AlbumViewModel directly wraps the Album class (ViewModel wraps the Model) this is a common pattern.
Now we are ready to query the backend for real data. Our business logic or model code from Album.cs provides a convenient method to do this.
public static async Task<IEnumerable<Album>> SearchAsync(string searchTerm)
Calling this method will return an IEnumerable of Albums. We can call this every time the user's typing is throttled, get the data, then clear the list of ViewModels from the SearchResults ObservableCollection and enumerate each item returned adding an AlbumViewModel to the SearchResults for each Album. The UI will automatically update and represent the state of our ViewModel as we do this.
To implement this functionality, add the following code to MusicStoreViewModel.cs
private CancellationTokenSource? _cancellationTokenSource;
private async void DoSearch(string s)
{
IsBusy = true;
SearchResults.Clear();
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(s))
{
var albums = await Album.SearchAsync(s);
foreach (var album in albums)
{
var vm = new AlbumViewModel(album);
SearchResults.Add(vm);
}
}
IsBusy = false;
}
Before we run it, we will need to remove our old dummy data from the constructor of MusicStoreViewModel. Remove the following lines...
SearchResults.Add(new AlbumViewModel());
SearchResults.Add(new AlbumViewModel());
SearchResults.Add(new AlbumViewModel());
Now run the application and click the store button, then search for an artist or album name. If all has gone to plan you should see the progressbar animating whilst the server is busy processing the request and then you should see some results appear in the list.